 ANNUAL REPORT 2020
ANNUAL REPORT 2020
We are acting in line with the Paris Agreement to avoid climate change and the consequences of a global increase in temperature above 2 degrees over pre-industrial levels.
This sustainable future means facing the challenges that range from the optimisation and purification of water used in the production process, a better use and reuse of raw materials and an efficient use of energy and renewable energy.
MATERIAL ASPECTS |
|
OUR COMMITMENT TO SDG |
|
|
We invest in technologies in the search for decarbonisation, such as the installation of energy equipment with the capacity to use green hydrogen at Cáseda. |
|
Viscofan invests in technologies that enable production with less production waste, and it also seeks to reduce the intensity of waste at landfills |
|
We carry out a sustainable management of water by investing in technology with reduced water withdrawal requirements. We invest in water purification facilities to improve discharge quality. |

Environmental management
The Group has a Sustainability Action Plan for the period 2019-2021, which seeks to promote the development of a culture of best sustainability practices, especially in the area of environment, with commitments for 2030 to reduce waste and CO2 emissions per metre produced.
Climate change is a significant aspect identified in the materiality analysis and, as such, is included in the Group’s long-term operating management processes. It forms an integral part of our risk mitigation and an essential part of our Sustainability Action Plan.
The governance and management of climate change at Viscofan is the responsibility of the Board of Directors and, by extension, of the Appointments, Remunerations and Sustainability Committee of the Board itself.
This Committee promotes and supervises compliance with environmental sustainability policies, overseeing their improvement and that they take into account the legitimate interests of the stakeholders.
Viscofan has a Sustainability Committee responsible for coordinating and supervising the long-term objectives, initiatives and work plans established by it in the sustainability area. Likewise, the Committee is part of the Group’s risk control system in the assessment and management of climate change risks and opportunities.
It is a mainstream committee comprising the Group’s CEO, the General Manager of Spain, the Chief Operations Officer, the Chief Commercial Officer, the Chief Human Resources Officer, the Chief Legal Officer and the Chief Investor Relations and Communication Officer.
Moreover, management of environmental matters at Group level is the responsibility of the Corporate Environment, Health and Safety (EHS) Department, which reports to the Operations Department and is responsible for coordinating and supervising EHS matters at all the Group’s production plants.
Climate change management is regulated in the Climate Change Policy, approved by the Board of Directors in 2020, and which demonstrates the Group’s commitment to this huge environmental problem, establishing its undertaking to control greenhouse emissions, energy efficiency and to a business strategy related with the development of alternative energy sources.
Furthermore, the internal climate change regulations complemented by the Environmental Policy, approved by the Board of Directors in 2020, stipulate that the Group’s measures must be adopted with respect for the environment, which means incorporating sustainable development criteria in all areas of activity, guaranteeing the efficient management of natural resources and minimising the undesirable effects of the Group’s activities.
In addition, the Group has a Sustainability Action Plan for the period 2019-2021, which seeks to promote the development of a culture of best sustainability practices, especially in the area of environment, with commitments for 2030 to reduce waste, water withdrawal and CO2 emissions per metre produced.
To attain long-term goals and control climate-related matters, Viscofan has quarterly environment indicators and each Group factory reports its main environmental indicators to central headquarters, such as energy, water and raw materials consumption and waste production. This information is used to calculate the whole Group’s carbon footprint and compliance with its environmental objectives.
Climate change is a risk identified in the Global Risk Map, since its implications may hinder the achievement of long-term objectives and the creation of value for stakeholders.
The main climate change implications for Viscofan are as follows:
Viscofan’s integral risk management system assesses and monitors the risks and their tendency, taking the necessary management measures which, aside from mitigating the risk, may generate opportunities. The main opportunities identified are as follows:
Viscofan’s commitment to the fight against climate change is also revealed in its human, operating and financial dimensions.
Management systems
Environmental. ISO 14.001:
We are working to attain this environmental management certification at all our production plants. Currently, more than 60% of the plants have this certificate (excluding the acquisitions made in the strategic period, 86% of the Group’s plants have this certificate).
In 2020, the Danville and Montgomery plants in the United States made progress in the certification process of their environmental management systems with regard to such regulation, with said certificate expected to be obtained in the first half of 2021. Likewise, the process at the New Jersey plant, acquired in December 2019, is expected to be performed in 2021.
The breakdown of the Group’s plants with ISO 14001 certificate is the following:
Country |
Plant |
ISO 14.001 |
Spain |
Cáseda |
|
|
Urdiain |
|
Germany |
Weinheim |
|
Serbia |
Novi Sad |
|
Czech Republic |
Ceske Budejovice |
|
Belgium |
Hasselt |
|
USA |
Kentland |
|
|
Danville |
2021 e |
|
Montgomery |
2021 e |
Mexico |
Zacapu |
|
|
San Luis Potosi |
|
Brazil |
Itu |
|
|
Matarazzo |
|
Uruguay |
Pando |
|
China |
Suzhou (2 plantas) |
|
Australia |
Sidney |
|
New Zealand |
Wellington |

Environmental investment in 2020
ISO 50.001 energy efficiency certificates
The Cáseda and Weinheim plants have an ISO 50.001 standard certificate, enabling the plants to improve their efficiency, energy costs and greenhouse emissions. In 2021, a project is envisaged at the Ceske Budejovice plant in the Czech Republic to obtain this certificate.
Other certificates
In 2020, the Ceske Budejovice plant in the Czech Republic obtained the ISCC Plus certificate for plastic casings. This certification system ensures the sustainability of raw materials and products for diverse markets.
Environmental investment
Part of Viscofan’s industrial asset base relates to environmental management, seeking the best available technology in the management of water, energy and waste, among others. Hence, at the end of December 2020, the gross value of this type of asset was €57.3 million (€54.2 million at 31 December 2019).
Viscofan continues to improve environmental management and with this objective in mind, in 2020, it increased investment in this area with €9.2 million (€6.5 million in 2019), representing 16% of the Group’s total investment. The most relevant investments in this area in 2020 are: the installation of co-generation engines with green hydrogen capacity in Cáseda (Spain), the improvement of water purification in Cáseda and Pando (Uruguay), and the installation of a system for improved energy management in Weinheim (Germany).
There is more information about the economic resources allocated to the protection of the environment in note 25 of the consolidated annual accounts.
Environmental training
Being more sustainable and reducing our impact on the environment is a commitment for all of us. In addition to allocating financial resources, measures are also promoted to further the Group’s values and commitments with regard to environmental management among employees, with training courses standing as an essential element of the management approach.

The fight against climate change is a global task. As an energy-intensive company, Viscofan is committed to energy efficiency and global climate protection. We seek to reduce the intensity of our atmospheric emissions by investing in and developing more efficient production technology, increasing the use of renewable energy and leading the change in the industry towards technology that helps to fight against climate change. We also wish to positively influence the value chain, through sustainable casings that help our customers to reduce their emissions.
Casing production is an on-going process all year round that requires a lot of heat, especially in the drying processes of casings. The main energy input used in the process is natural gas, electricity and steam. The reduction in energy consumption with new technologies and the availability of renewable energy sources are essential aspects of Viscofan’s undertaking to contribute to climate change protection and, hence, Viscofan works on three main axes
Energy efficiency management at the Viscofan Group is expressed in internal energy audits and its corresponding improvement plans are encompassed within the Sustainability Action Plan. Viscofan has its own energy management system to monitor, follow up and control energy consumption.
The internal energy consumption expressed in Giga Wh and the energy intensity, with a 100 baseline year of 2018, is the following:
| Energy consumption |
2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
| Gigavatt-hour (GWh) | 94 | 102 | 100 |
| Energy intensity. Base 100 year 2018 |
2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
| Consumption in GWh /Meters produced | 2,371 | 2,294 | 2,276 |
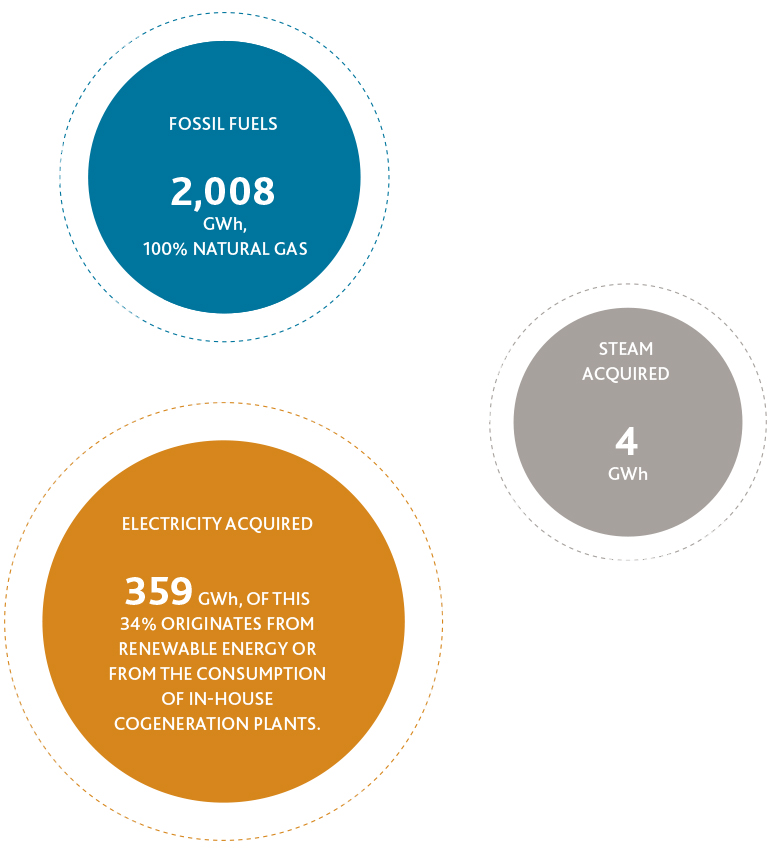
In 2020, internal energy consumption increased by 3.4% with respect to 2019 in a context of increased production activity. Viscofan’s energy consumption in 2020 was broken down into:
However, the consolidation of energy optimisation projects in previous years and the implementation of new projects enables Viscofan to grow in terms of revenue and production, reducing its energy intensity. Noteworthy is the new fibrous and cellulose casing production technology in Cáseda.
The breakdown of direct and indirect CO2 emissions and their intensity is as follows:
| CO2 Emissions Tn |
2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
| Direct | 397,959 | 386,221 | 378,128 |
| Indirect | 165,228 | 154,580 | 164,138 |
| TOTAL | 563,188 | 540,801 | 542,266 |
| Base 100 year 2018 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
| CO2 Emissions intensity |
94 | 101 | 100 |
| Others Emissions Tn |
2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
| NOX | 713 | 657 | 643 |
| SOX | 29 | 32 | n.d. |
| Million € |
2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
| Revenue | 912.2 | 849.7 | 786.0 |
| Ratio (emissions in tns / revenue in millions €) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
| CO2 Emissions | 617.4 | 636.5 | 689.9 |
| NOX | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.82 |
| SOX | 0.03 | 0.04 | n.d. |
Absolute CO2 emissions may be affected by the variation in the product family and geographical production mix, and the inclusion of new companies in the consolidation scope.
They may also feel the impact of the availability and production of electricity from cogeneration engines. As a whole, the engines enable the company to avoid CO2 emissions, since they enable electricity to be produced in a more efficient fashion, and one part is used internally and another is sold in the grid.
In 2020, direct and indirect emissions increased due to the rise in production; however, their intensity on the extruded metres is reduced due to the consolidation of the energy optimisation projects carried out in previous years and the implementation of new projects. Noteworthy was the new fibrous and cellulose casing production technology in Cáseda.
Within the commitment to reduce the intensity of CO2 emissions and the on-going search for efficient operations, the following projects were carried out:
In 2020, two cogeneration engines were installed in Cáseda with increased efficiency from an energy and environmental standpoint. The new energy equipment replaces part of the existing equipment and has the ability to use green hydrogen, a renewable energy that still cannot be employed in an efficient on-going manner. However, within its commitment to fight against climate change, Viscofan wishes to boost its development with investments and is cooperating with government entities and energy sector companies.
New production lines are being installed at the Cáseda plant using new fibrous technology which, among other aspects, is a more efficient form of energy.
Viscofan is involved in talks with public entities in Spain to be able to include cellulose casings as a source of biomass, a category not regulated under current Spanish legislation. At the converting plant in Suzhou (China), a new boiler was installed which works with electricity as opposed to the former boiler that required fossil fuel, thereby enabling the plant’s energy requirements to be met with fewer CO2 emissions.
Within the Group’s objective is to promote the use of renewable energy - in 2020, in Mexico, all energy consumed at the San Luis Potosí plant and 50% of the energy consumed at the Zacapu plant was generated from renewable sources. Likewise in 2020, electricity from the centres located in Tajonar, Cáseda and Urdiain, was classified as green energy, which means that 100% of this energy was of a renewable origin and of high efficiency co-generation. Also, in 2020, solar panels began to be installed at the Urdiain converting plant (Spain). Hence, in total, 34% of the electricity acquired by Viscofan originates from renewable energy sources.
Electricity production through co-generation
In 2020, Viscofan avoided the emission of CO2 into the atmosphere by using cogeneration compared to that theoretically emitted to produce the steam obtained in cogeneration using conventional boilers, at the plants in Cáseda (Spain) and Weinheim (Germany). Below is a detail of the equivalent tonnes of CO2 avoided:
| 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | |
| CO2 avoided by energy optimization | 90,449 | 90,531 | 91,715 |
Thanks to co-generation installed, it is worth noting that over the last 10 years, the Viscofan Group has managed to avoid the emission of nearly one million tonnes of CO2 into the atmosphere.
As signatory member of the United Nations Global Compact, Viscofan is committed to SDG 13. Climate action. This commitment has been materialized with a long term-target (2030) of a 30% reduction in scope 1 and 2 CO2 emissions over a million extruded metres with respect to 2018.
The variations in the ratio on a baseline of 100 for 2018 are as follows:
| Base 100 year 2018 | Commitment 2030 |
2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
| CO2 emissions scope 1 and 2 / Extruded meters |
70 | 94 | 101 | 100 |

Water is essential for life and also for the viability of Viscofan’s business, since the casing production process and a large part of raw materials used depend on water. We acknowledge that it is a resource whose availability is affected by climate change and by a growing global demand.
Viscofan’s production plants require water withdrawal for different phases of the process, such as the washing of casings, refrigeration, steam production and the moistening of said casings.
At Viscofan, during the production of casings, 20% of the water withdrawal is evaporated, is incorporated into the product or is consumed, while the remaining 80% is taken to purification plants installed at Viscofan’s production plants to be processed before being returned to freshwater surfaces, or is discharged to municipal processing plants.
Viscofan’s water management focuses its efforts two-fold. Firstly by seeking production technology with a lower water requirement, mainly in phases of the process that involve the washing of casings. Once the water has been used, Viscofan works to improve the quality of the water that we discharge even further and to understand the risks associated with the availability and use of water in the areas in which we operate.
| Intensity rate. Base 100 year 2018 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
| Water withdrawal in m3 / Meters extruded | 100 | 101 | 100 |
| 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | |
| Surface water | 4,107,250 | 3,849,469 | 3,755,026 |
| Ground water | 2,756,290 | 2,643,301 | 2,636,088 |
| Local water supply | 3,515,107 | 2,947,574 | 3,021,961 |
| Rainwater | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Waste water | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 10,378,646 | 9,440,345 | 9,413,076 |
| 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | |
| Surface water | 39.6% | 40.8% | 39.9% |
| Ground water | 26.6% | 28.0% | 28.0% |
| Local water supply | 33.9% | 31.2% | 32.1% |
| Rainwater | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Waste water | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| TOTAL | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | |
| Water reused in m3 |
15,172 | 1,069 | 26,635 |
In 2020, Viscofan increased production activity to satisfy a greater demand in casings, requiring increased water withdrawal with 10.4 million metres3 as opposed to 9.4 million metres3 in 2019.
However, the water withdrawal intensity ratio per metre produced dropped by 1.6% in 2020 as opposed to 2019. The consolidation of projects to optimise the use of water and those performed in 2020 have helped to achieve this improvement. Of note:
To increase water optimisation, in 2018, a project was implemented to re-use water in Suzhou (China), although the outcome did not meet expectations and the project was cancelled due to the decision to improve the discharge quality at the plant. In 2020, a new project was commenced at the Pando plant (Uruguay), enabling the volume of water reused at the Group to be increased with respect to 2019.
All captures are strictly regulated by the public sector, which assign permits and determine the maximum permitted withdrawal volumes to preclude significant effects. Hence, there was no record in 2020 of the organisation’s water collection activities significantly affecting any water sources.
According to the World Resources Institute list, the plants in Belgium and Mexico are located in areas of high or extremely high water stress, a risk that the Group has identified. They account for 7% of total water withdrawal and 8% of the Viscofan Group’s total water discharge in 2020. In the year, problems of water supply were not declared in these areas.
Protecting the quality of the water that we discharge into the tributaries is one of Viscofan’s commitments. Adequate water management also includes correctly purifying its wastewater and minimising the impact of its activities on the environment, thus, we apply the best available technologies in an on-going process such as that of the Group.
Accordingly, Cáseda’s purification plant is an example of best practices within the Group. This facility allows the biological quality of the Aragón River as it passes by the plant to be improved. According to a study performed by a third party (Ekolur) in 2020, in June and August, the upstream waters (before the plant) of the river have the Class II rating or a good biological quality rating, and downstream (after the plant), the river improves its Class I or high biological rating.
Viscofan fosters investment in water treatment facilities. In 2020, a new ozone facility was implemented to reduce salt from discharges at its Cáseda plant (Spain). Likewise, the Group has water purification plants at its manufacturing facilities, where the treatment of water makes it possible to improve the quality of discharges. Factories that treat 100% of the water are: Cáseda (Spain), Zacapu (Mexico), Koteks (Serbia), Itu (Brazil), Pando (Uruguay) and Suzhou (China).
Water discharge broken down by destination is as follows:
| 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | |
| Surface freshwater | 4,588,313 | 4,354,863 | 4,279,567 |
| Local treatment plant | 3,682,863 | 3,405,950 | 3,387,789 |
| TOTAL | 8,271,176 | 7,760,813 | 7,667,357 |
| 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | |
| Surface freshwater | 55.5% | 56.1% | 55.8% |
| Local treatment plant | 44.5% | 43.9% | 44.2% |
| TOTAL | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
As signatory member of the United Nations Global Compact, Viscofan is committed to SDG 6. Clean water and sanitation. This commitment has been materialized with a long term-target (2030) of a 10% reduction in water collection over a million extruded metres with respect to 2018.
The variations in the ratio on a baseline of 100 for 2018 are as follows:
| Base 100 year 2018 | Commitment 2030 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
| Water withdrawal in m3 / Meters Extruded |
90 | 100 | 101 | 100 |

Population growth influences the availability of the planet’s resources, and the efficient use of such resources and the quest for a circular economy are essential. A global challenge that requires environmental criteria to be included throughout the whole value chain to minimise the impact of Viscofan’s activities
Population growth influences the availability of the planet’s resources, and the efficient use of such resources and the quest for a circular economy are essential. A global challenge that requires environmental criteria to be included throughout the whole value chain to minimise the impact of Viscofan’s activities. The customized casing production process transforms raw materials by mechanical and chemical means, leading to waste generation. Working in conjunction with the whole value chain, Viscofan promotes the sustainable use of resources. Firstly, through the selection, search and approval of raw materials, which are then transformed by mechanical and chemical means, producing millions of metres of casing per year. In this process, Viscofan is constantly searching for more efficient technology, which involves a reduced generation of waste, encouraging its circularisation. Lastly, Viscofan’s product innovation helps and encourages the innovation of meat producers in the search for more sustainable products
Over 84% of our revenue comes from natural, biodegradable or recycled material casings and the rest corresponds to plastic casings of a synthetic nature. In the selection of raw materials, we seek to reduce their environmental impact as much as possible:
Viscofan is constantly searching for more efficient production technology that will enable, inter alia, a reduction in production waste. Furthermore, as established by the Environmental Policy, the concept of circular economy is included in the decision-making processes on investments and in the planning and execution of activities.
In this regard, it must be stressed that in 2020, Cáseda’s new technology contributed to reduce waste due to fewer remains in the production process in its first full year of production. Also, in the collagen casing business line acquired in 2019 in North America, Viscofan is installing a more efficient production
In 2020, the tonnes of waste rose in a context of increased production activity, although the percentage of composted waste improved with respect to the previous year
One of the goals established in the Sustainability Action Plan is to reduce the tonnes of waste at landfills, seeking circular alternatives. In this regard, in 2020, the landfill waste ratio fell with respect to production, and waste valorization improved with an increased percentage of composted discharges. In a context of improvement, different alternatives continue to be explored, especially in the area of waste valorization.
| 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | |
| Waste in tonnes (tns) | 57,344 | 49,307 | 53,423 |
| Waste in tn./ Meters produced. Base 100, year 2018 | 97 | 93 | 100 |
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||
| Non-hazardous |
Hazardous |
TOTAL | Non-hazardous |
Hazardous |
TOTAL | |
| Reused | 5.8% | 0.0% | 5.8% | 5.9% | 0.0% | 6.0% |
| Recycled | 8.6% | 0.4% | 9.0% | 7.8% | 2.5% | 10.2% |
| Composted | 29.9% | 0.0% | 29.9% | 27.8% | 0.0% | 27.8% |
| Recovered | 1.7% | 0.0% | 1.7% | 1.8% | 0.2% | 2.0% |
| Incinerated | 6.6% | 0.4% | 7.0% | 7.7% | 0.2% | 7.9% |
| Landfill | 34.5% | 1.6% | 36.1% | 36.6% | 1.3% | 37.9% |
| Other | 2.9% | 7.5% | 10.4% | 1.6% | 6.5% | 8.2% |
| TOTAL | 90.1% | 9.9% | 100.0% | 89.2% | 10.8% | 100.0% |
For the management of the waste generated in our production process, we use disposal methods that have been determined locally based on local regulations and good practices within the Group, taking into consideration the characteristics of the production process and the raw materials used.
Moreover, the Viscofan Group has implemented an environmental management system with a view to preventing leaks, in which it has established management mechanisms and technical control elements. There were no leaks at Viscofan Group facilities in 2020 that had to be reported to the competent authorities, understood to be those that cause damage to the external area of the facility and must be reported to the corresponding administration.
As signatory member of the United Nations Global Compact, Viscofan is committed to SDG 12. Responsible consumption and production. This commitment has been materialized with a long term-target (2030) of a 30% reduction in tonnes of landfill waste over a million extruded metres with respect to 2018.
The variations in the ratio on a baseline of 100 for 2018 are as follows:
| Base 100 year 2018 | Commitment 2030 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
| Landfill waste in tonnes / Extruded meters | 70 | 90 | 91 | 100 |
Likewise, the reduction in the intensity of landfill waste was tied to the Long-Term Incentives Plan aimed at executive directors, executives and key personnel. It is proposed to apply 30% to the weighting ratio on attaining a minimum reduction in the indicator of 4 percentage points and to increase the weighting ratio up to 100% if the indicator is reduced to 10 percentage points in the measurement period.
In 2020, the Viscofan Group had not received any environmental fines.
Before starting...
We use our own and third-party cookies for analytical purposes and to show you personalized advertising based on a profile prepared from your browsing habits (for example, pages visited). Click HERE for more information. You can accept all cookies by pressing the "Accept" button or configure or reject their use by pressing the "Configure" button.
ACCEPT AND CONTINUE Set cookies